Note: This blog post was written for the module Enterprise IT (113601a).
Introduction
Demand forecasting is all about estimating the future demand for a product or service. The automotive industry operates in highly volatile markets with complex supply chains, making demand forecasting a critical challenge. Recent developments, such as fluctuating sales, changing regulatory requirements and potential trade tariffs, have further increased the uncertainty in automotive industry. Additionally, consumer demand is influenced by multiple factors, including pricing, vehicle quality and technological advancements, making accurate demand forecasting more difficult than ever.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further exposed the fragility of supply chains, especially in the procurement of critical components like semiconductors and battery technologies. Supply chain bottlenecks have had a major impact on production and demand forecasting, highlighting the urgent need for more adaptive forecasting models [1].
Given the importance of accurate forecasting for supply chain efficiency, businesses must adopt more advanced forecasting techniques to anticipate market trends and optimize operations [2]. In the automotive sector, accurate demand forecasting helps companies to manage inventory effectively, adjust pricing strategies, and plan vehicle discounts. While traditional regression-based models have been widely used for forecasting, they struggle to produce reliable results in rapidly changing market conditions [3].
To address these challenges, the automotive industry requires forecasting methods that are both highly adaptable and precise. AI/ML-based techniques, such as neural networks, provide better accuracy and pattern recognition capabilities, making them a promising alternative to traditional models [4].
Traditional Demand Forecasting Approaches
One of the most used forecasting methods in the automotive sector is time series forecasting, particularly in Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) production planning and aftermarket inventory management [4]. Time series forecasting involves collecting data points recorded in chronological order [5, 6], with models like ARIMA (Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average) and SARIMA (Seasonal ARIMA) being commonly applied. ARIMA predicts future values based on historical data, assuming that past demand trends are reliable indicators of future demands [7]. SARIMA extends ARIMA by including seasonal demand variations in the forecasting process [8].
ARIMA consists of three key components:
- AR (Auto Regression) – Uses past values to predict future ones.
- I (Integrated) – Differencing is applied to make the series stationary.
- MA (Moving Average) – Accounts for past forecast errors to improve accuracy.
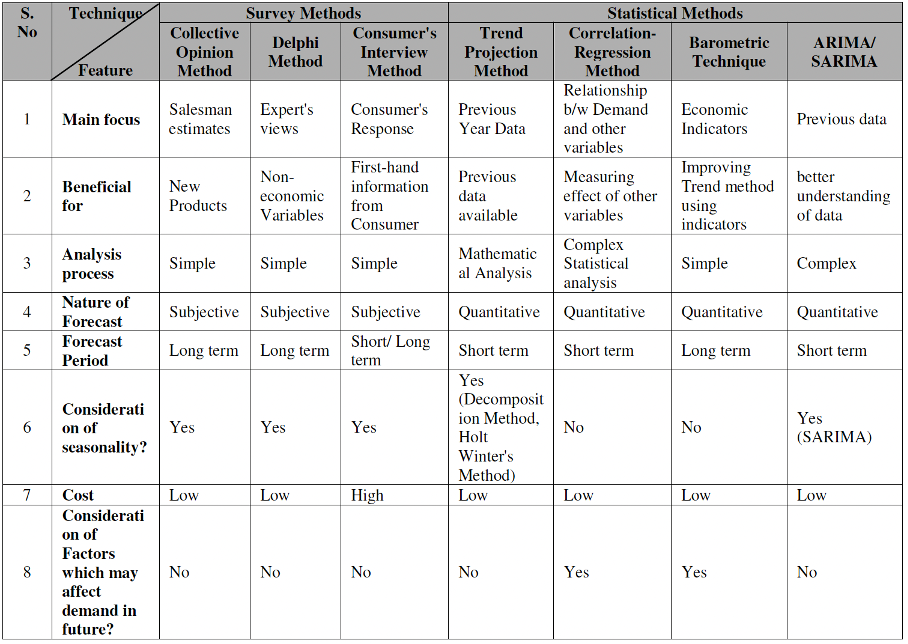
Figure 1. Analysis of traditional demand forecasting methods. [9]
Other traditional demand forecasting methods have their own strengths, but they all have strong dependence on historical data [9]. They assume that past patterns will repeat, making them ineffective when demand changes suddenly. This limitation is especially problematic in the automotive industry, where accurate forecasting is essential to reduce excess inventory, prevent stock shortages and improve supply chain efficiency [4, 7].
AI/ML-based Demand Forecasting Approaches
To address the shortcomings of traditional methods, non-traditional forecasting techniques now leverage AI/ML tools. Unlike traditional forecasting models, which rely on static data and fixed relationships, AI/ML based models continuously learn from new data, adjust to new information, and provide real-time predictions.
Recent studies have shown that machine learning techniques, such as Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, improve the accuracy of demand forecasting [10]. LSTM, a type of Recurrent Neural Network (RNN), is particularly effective at learning long-time dependencies and predicting sequential data with high accuracy [11]. Figure 2 shows an example of how LSTM works.
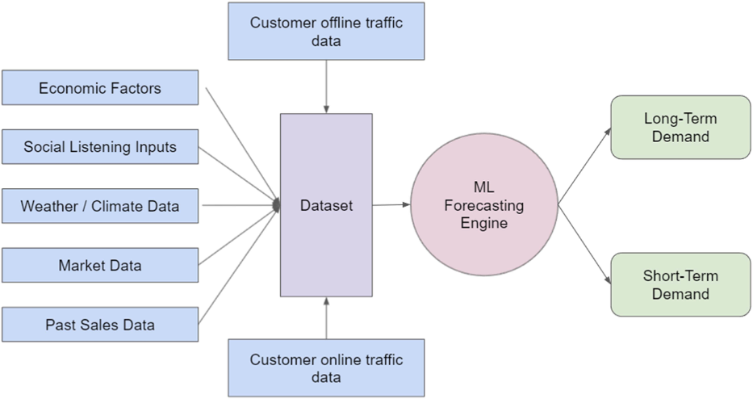
Figure 2. Example functional diagram of LSTM for demand forecasting [7].
LSTM-based models offer several advantages, including:
- Enhanced productivity by optimizing inventory levels.
- Real-time data processing for customer behavior analysis.
- Multi-level decision-making support for production and supply chain management [7].
Apart from LSTM, there are other AI/ML-based demand forecasting approaches. Neural Networks detects complex patterns in large datasets, while Fuzzy Logic helps process imprecise or incomplete information. Genetic Algorithms improve forecast accuracy by using evolutionary mechanisms. Bayesian approaches continuously update forecast with new data, and Wavelet Transforms combined with Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) further refine forecast accuracy [9].
The figure 3 presents a comparative analysis, highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches.
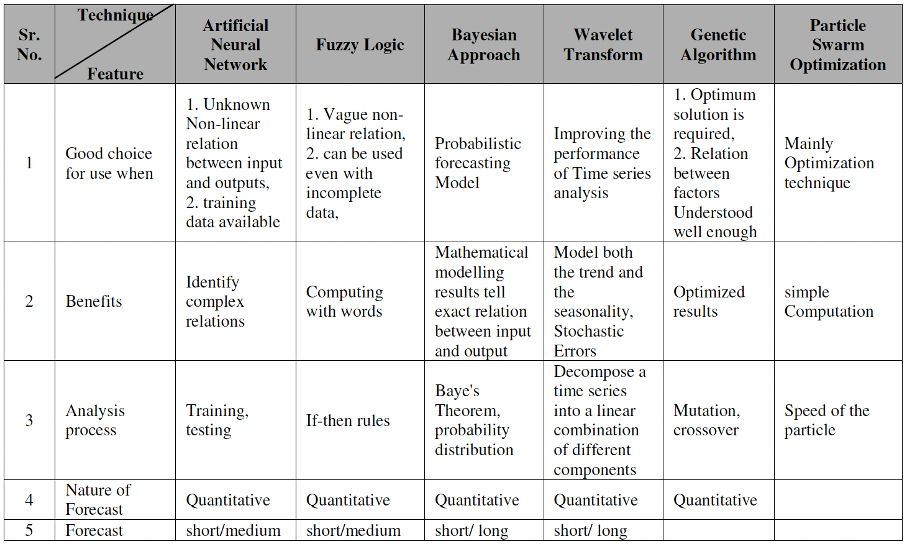
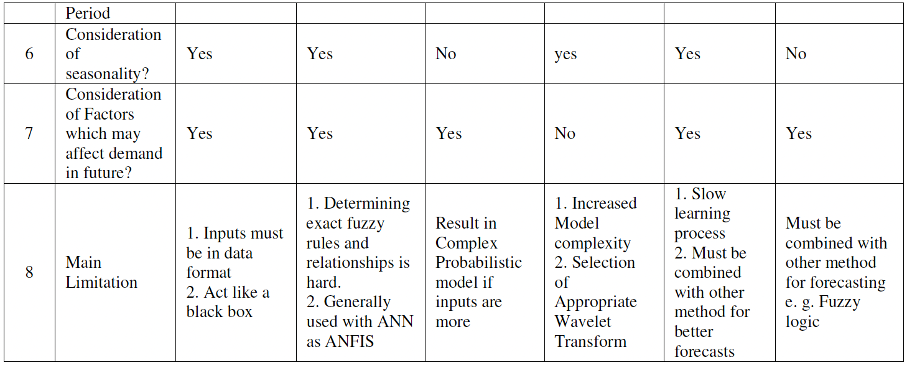
Figure 3. Analysis of AI/ML based demand forecasting models. [9]
AI/ML-based forecasting models are especially beneficial in automotive industry as demand is highly variable and real-time decision-making is crucial. They enable enterprises to anticipate market trends, optimize inventory management, and improve supply chain efficiency [4, 11]. With its enhanced accuracy, adaptability, and automation, AI/ML-based demand forecasting is becoming a critical tool for businesses operating in dynamic and unpredictable environments.
Challenges and Limitations in Implementing AI/ML-based Demand Forecasting Approaches
Even though AI and machine learning improve demand forecasting, their implementation comes with several challenges:
- Data Quality – AI models require high-quality, well-integrated data to deliver good predictions. Inaccurate, incomplete, or inconsistent data reduces forecasting accuracy and leads to unreliable decision-making [15]. Poor data quality may result from manual data entry mistakes, missing values, outdated data, or system inconsistencies. In the automotive industry, data is often scattered across different departments, like manufacturing, sales, supply chain, and aftersales services, making integration harder [12, 13]. Without a standardized data infrastructure, AI/ML-based models may struggle to handle real-world complexities, leading to poor forecasting and inventory problems [14].
- Complexity and Scalability – The automotive industry’s supply chain is highly complex, involving many suppliers, manufacturers, and logistic providers [7]. AI/ML-based forecasting must consider many interconnected factors, requiring scalable models that can handle large data volumes while remaining adaptable [12].
- Dependency on Real-Time Data – AI/ML improves decision-making, but accessing accurate, up-to-date data is not always possible due to system delays, data collections issues and processing limitations [16]. When real-time data is unavailable, the forecasts may be unreliable.
AI/ML based demand forecasting is mainly used by large automotive, as small manufacturers and those in developing countries face challenges such as limited data, budget constraints, and scalability issues. Advanced AI models require high cost, making them less accessible to smaller businesses [17].
Beyond technical challenges, the adoption of AI also raises ethical, financial and regulatory concerns. For AI to be sustainable in the long run, companies must prioritize trust, transparency, and regulatory compliance [18]. As AI continues to evolve, its impact on automotive production, supply chains, and business plans will depend on how well these challenges are addresses.
Conclusion
Traditional forecasting models, which rely on historical data and static assumptions, are less effective in dynamic market environments. In contract, AI/ML-based forecasting is dynamic, continuously updated, and improves forecasting accuracy, operational efficiency, and cost-effectiveness concerning inventory management of parts and vehicles.
However, AI/ML-based demand forecasting also comes with its own set of challenges, particularly in data management and integration with enterprise IT systems. Therefore, choosing the right forecasting method depends on balancing accuracy, complexity, and practical implementation. By selecting suitable forecasting approaches, companies can enhance decision-making, improve operational efficiency, and remain competitive in an unpredictable market.
Quellen
[1] Frieske, B., & Stieler, S. (2022). The “Semiconductor Crisis” as a Result of the COVID-19 Pandemic and Impacts on the Automotive Industry and Its Supply Chains. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 13(10), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj13100189
[2] Toorajipour, R., Sohrabpour, V., Nazarpour, A., Oghazi, P., & Fischl, M. (2020). Artificial intelligence in supply chain management: A systematic literature review. Journal of Business Research, 122, 502–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.09.009
[3] Kamal, E., Abdel-Gawad, A. F. A., Ibraheem, B., & Zaki, S. (2023). Machine Learning fusion and data analytics Models for demand forecasting in the automotive industry: A Comparative study. Fusion Practice and Applications, 12(1), 24–37. https://doi.org/10.54216/fpa.120102
[4] Rožanec, J. M., Kažič, B., Škrjanc, M., Fortuna, B., & Mladenić, D. (2021). Automotive OEM Demand Forecasting: A Comparative Study of Forecasting Algorithms and Strategies. Applied Sciences, 11(15), 6787. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11156787
[5] Chatfield, C. (2000). Time-Series Forecasting. In Chapman and Hall/CRC eBooks. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420036206
[6] Shumway, R. H., & Stoffer, D. S. (2005). Time Series analysis and its applications (Springer Texts in Statistics). In Springer eBooks. https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1088844
[7] Singh, S., Yadav, B., & Batheri, R. (2023). Industry 4.0: Meeting the challenges of demand sensing in the automotive industry. IEEE Engineering Management Review, 51(4), 179–184. https://doi.org/10.1109/emr.2023.3292331
[8] Douaioui, K., Oucheikh, R., Benmoussa, O., & Mabrouki, C. (2024). Machine learning and deep learning models for demand forecasting in supply chain management: A critical review. Applied System Innovation, 7(5), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/asi7050093
[9] Kumar, V. & Kumar, R., 2019. THE DEMAND FORECASTING: A COMPARATIVE REVIEW OF. International Journal of Mechanical and Production, 9(1), pp. 253-262.
[10] Phyu, M. M., & Khine, M. T. (2023). Retail demand forecasting using sequence to sequence long short-term memory networks. IEEE Conference on Computer Applications (ICCA), 208-213. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCA51723.2023.10181450
[11] Afandizadeh, S., Sharifi, D., Kalantari, N., & Mirzahossein, H. (2023). Using machine learning methods to predict electric vehicles penetration in the automotive market. Scientific Reports, 13(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-35366-3
[12] AllSTARSIT. (n.d.). AI in supply chain management of the automotive industry. Retrieved February 13, 2025, from https://www.allstarsit.com/blog/ai-in-supply-chain-management-of-the-automotive-industry
[13] PlanetTogether. (2025). Overcoming data silos in AI-powered supply chain planning: Unlocking the full potential of integration. Retrieved February 13, 2025, from https://www.planettogether.com/blog/overcoming-data-silos-in-ai-powered-supply-chain-planning-unlocking-the-full-potential-of-integration
[14] dotData. (2022). How an automobile manufacturer saved $10M per year with AI. Retrieved February 16, 2025, from https://dotdata.com/blog/how-an-automobile-manufacturer-saved-10m-per-year-with-ai/
[15] Pacemaker AI. (n.d.). Demand forecasting meets artificial intelligence. Retrieved February 16, 2025, from https://www.pacemaker.ai/en/blog/demand-forecasting-meets-artificial-intelligence
[16] McKinsey & Company. (2022). AI-driven operations forecasting in data-light environments. Retrieved February 18, 2025, from https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/operations/our-insights/ai-driven-operations-forecasting-in-data-light-environments
[17] The Manufacturer. (2024). The challenges preventing AI adoption in manufacturing. Retrieved February 19, 2025, from https://www.themanufacturer.com/articles/the-challenges-preventing-ai-adoption-in-manufacturing/
[18] Taylor Wessing. (2024). EU AI Act and the automotive industry – Legal challenges ahead. Retrieved February 21, 2025, from https://www.taylorwessing.com/en/interface/2024/ai-act-sector-focus/eu-ai-act-and-the-automotive-industry

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.